From Safe Counsel, 1900.
… it was by no means uncommon to see ‘a mother lay her daughter down upon the carpet, and, placing her foot upon her back, break half a dozen laces in tightening her stays.’
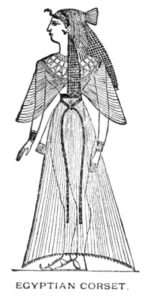 1. The origin of the corset is lost in remote antiquity. The figures of the early Egyptian women show clearly an artificial shape of the waist produced by some style of corset. A similar style of dress must also have prevailed among the ancient Jewish maidens; for Isaiah, in calling upon the women to put away their personal adornments, says: “Instead of a girdle there shall be a rent, and instead of a stomacher (corset) a girdle of sackcloth.”
1. The origin of the corset is lost in remote antiquity. The figures of the early Egyptian women show clearly an artificial shape of the waist produced by some style of corset. A similar style of dress must also have prevailed among the ancient Jewish maidens; for Isaiah, in calling upon the women to put away their personal adornments, says: “Instead of a girdle there shall be a rent, and instead of a stomacher (corset) a girdle of sackcloth.”
2. Homer also tells us of the cestus or girdle of Venus, which was borrowed by the haughty Juno with a view to increasing her personal attractions, that Jupiter might be a more tractable and orderly husband.
3. Coming down to the later times, we find the corset was used in France and England as early as the 12th century.
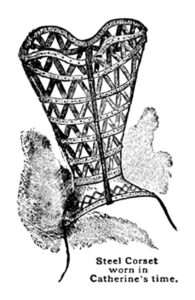 4. The most extensive and extreme use of the corset occurred in the 16th century, during the reign of Catherine de Medici of France and Queen Elizabeth of England. With Catherine de Medici a thirteen-inch waist measurement was considered the standard of fashion, while a thick waist was an abomination. No lady could consider her figure of proper shape unless she could span her waist with her two hands. To produce this result a strong rigid corset was worn night and day until the waist was laced down to the required size. Then over this corset was placed the steel apparatus shown in the illustration […]. This corset-cover reached from the hip to the throat, and produced a rigid figure over which the dress would fit with perfect smoothness.
4. The most extensive and extreme use of the corset occurred in the 16th century, during the reign of Catherine de Medici of France and Queen Elizabeth of England. With Catherine de Medici a thirteen-inch waist measurement was considered the standard of fashion, while a thick waist was an abomination. No lady could consider her figure of proper shape unless she could span her waist with her two hands. To produce this result a strong rigid corset was worn night and day until the waist was laced down to the required size. Then over this corset was placed the steel apparatus shown in the illustration […]. This corset-cover reached from the hip to the throat, and produced a rigid figure over which the dress would fit with perfect smoothness.
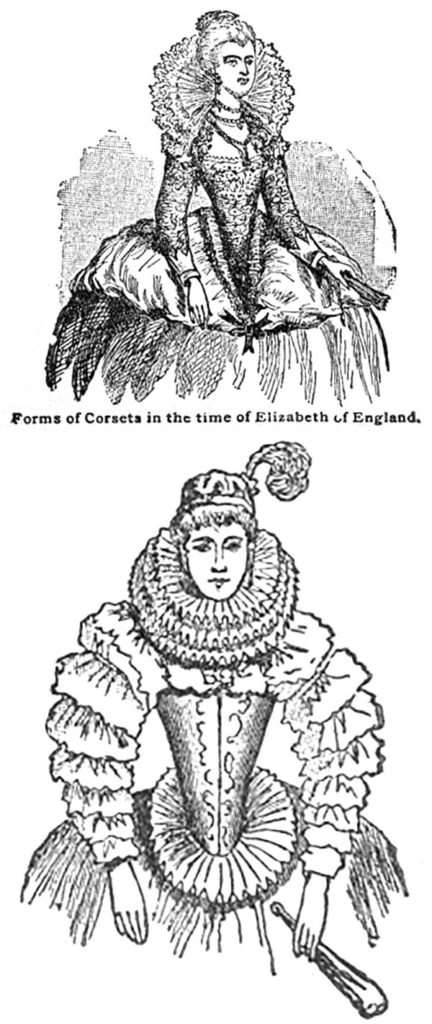
5. During the 18th century corsets were largely made from a species of leather known as “Bend,” which was not unlike that used for shoe soles, and measured nearly a quarter of an inch in thickness. One of the most popular corsets of the time was the corset and stomacher shown in the accompanying illustration.
6. About the time of the French Revolution a reaction set in against tight lacing, and for a time there was a return to the early classical Greek costume. This style of dress prevailed, with various modifications, until about 1810, when corsets and tight lacing again returned with threefold fury. Buchan, a prominent writer of this period, says that it was by no means uncommon to see “a mother lay her daughter down upon the carpet, and, placing her foot upon her back, break half a dozen laces in tightening her stays.”
 7. It is reserved to our own time to demonstrate that corsets and tight lacing do not necessarily go hand in hand. Distortion and feebleness are not beauty. A proper proportion should exist between the size of the waist and the breadth of the shoulders and hips, and if the waist is diminished below this proportion, it suggests disproportion and invalidism rather than grace and beauty.
7. It is reserved to our own time to demonstrate that corsets and tight lacing do not necessarily go hand in hand. Distortion and feebleness are not beauty. A proper proportion should exist between the size of the waist and the breadth of the shoulders and hips, and if the waist is diminished below this proportion, it suggests disproportion and invalidism rather than grace and beauty.
8. The perfect corset is one which possesses just that degree of rigidity which will prevent it from wrinkling, but will at the same time allow freedom in the bending and twisting of the body. Corsets boned with whalebone, horn or steel are necessarily stiff, rigid and uncomfortable. After a few days’ wear the bones or steels become bent and set in position, or, as more frequently happens, they break and cause injury or discomfort to the wearer.
9. About seven years ago an article was discovered for the stiffening of corsets, which has revolutionized the corset industry of the world. This article is manufactured from the natural fibers of the Mexican Ixtle plant, and is known as Coraline. It consists of straight, stiff fibers like bristles bound together into a cord by being wound with two strands of thread passing in opposite directions. This produces an elastic fiber intermediate in stiffness between twine and whalebone. It cannot break, but it possesses all the stiffness and flexibility necessary to hold the corset in shape and prevent its wrinkling.
We congratulate the ladies of to-day upon the advantages they enjoy over their sisters of two centuries ago, in the forms and the graceful and easy curves of the corsets now made as compared with those of former times.
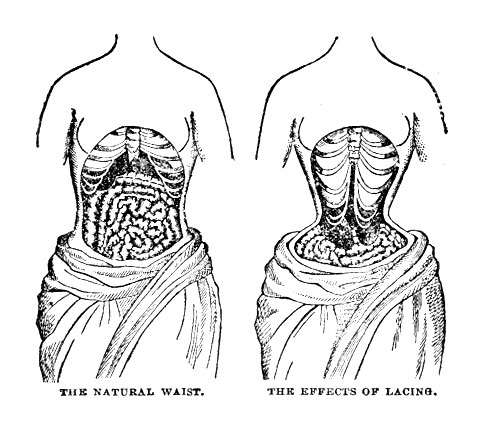 TIGHT-LACING.
TIGHT-LACING.
It destroys natural beauty and creates an unpleasant and irritable temper. A tight-laced chest and a good disposition cannot go together. The human form has been molded by nature, the best shape is undoubtedly that which she has given it. To endeavor to render it more elegant by artificial means is to change it; to make it much smaller below and much larger above is to destroy its beauty; to keep it cased up in a kind of domestic cuirass is not only to deform it, but to expose the internal parts to serious injury. Under such compression as is commonly practiced by ladies, the development of the bones, which are still tender, does not take place conformably to the intention of nature, because nutrition is necessarily stopped, and they consequently become twisted and deformed.
Those who wear these appliances of tight-lacing often complain that they cannot sit upright without them—are sometimes, indeed, compelled to wear them during all the twenty-four hours; a fact which proves to what extent such articles weaken the muscles of the trunk. The injury does not fall merely on the internal structure of the body, but also on its beauty, and on the temper and feelings with which that beauty is associated. Beauty is in reality but another name for expression of countenance, which is the index of sound health, intelligence, good feelings and peace of mind. All are aware that uneasy feelings, existing habitually in the breast speedily exhibit their signature on the countenance, and that bitter thoughts or a bad temper spoil the human expression of its comeliness and grace.















You must be logged in to post a comment.